Recorded Future analysts have noticed that hackers are using Google Tag Manager (GTM) containers to inject electronic skimmers that then steal bank card details and personal information from shoppers on e-commerce sites.
Let me remind you that we also talked about the E-Commerce Software Developer FishPig Hacked in a Massive Supply Chain Attack.
GTM is used on thousands of sites for various metrics, customer tracking, and other marketing purposes. GTM uses containers to embed JavaScript and other resources on websites, and criminals have learned to hide malicious scripts in GTM containers, which allows them to steal personal information from customers.
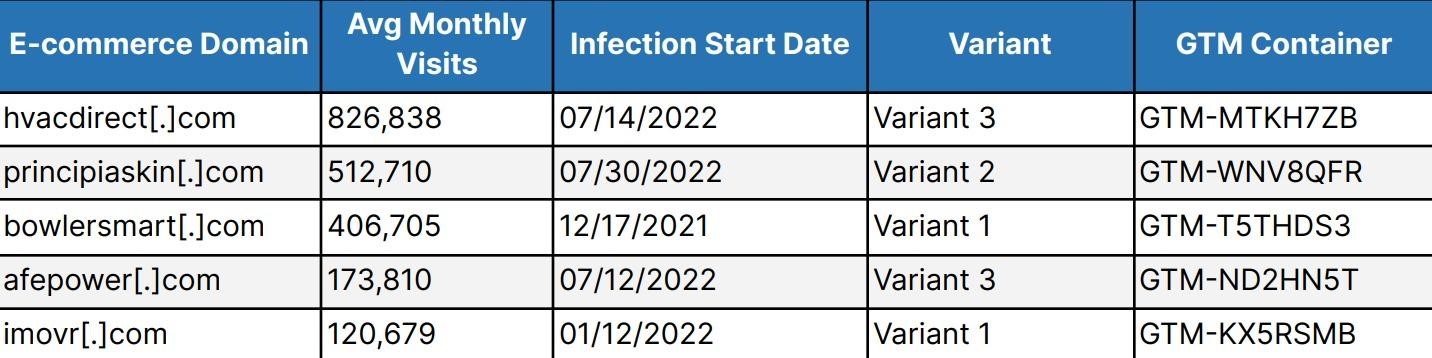
In total, the researchers found 569 e-commerce domains infected with web skimmers. According to the report, 314 of them were confirmed to be infected with GTM skimmers, while another 255 sent stolen data to malicious domains linked to GTM abuse.
As of August 25, 2022, almost 90 of those domains were still infected, and researchers say it takes administrators, on average, more than three months to fix a breach.
At the same time, experts note that, judging by the discussions on the darknet, the abuse of GTM began in 2018, and was already used by various hack groups then.
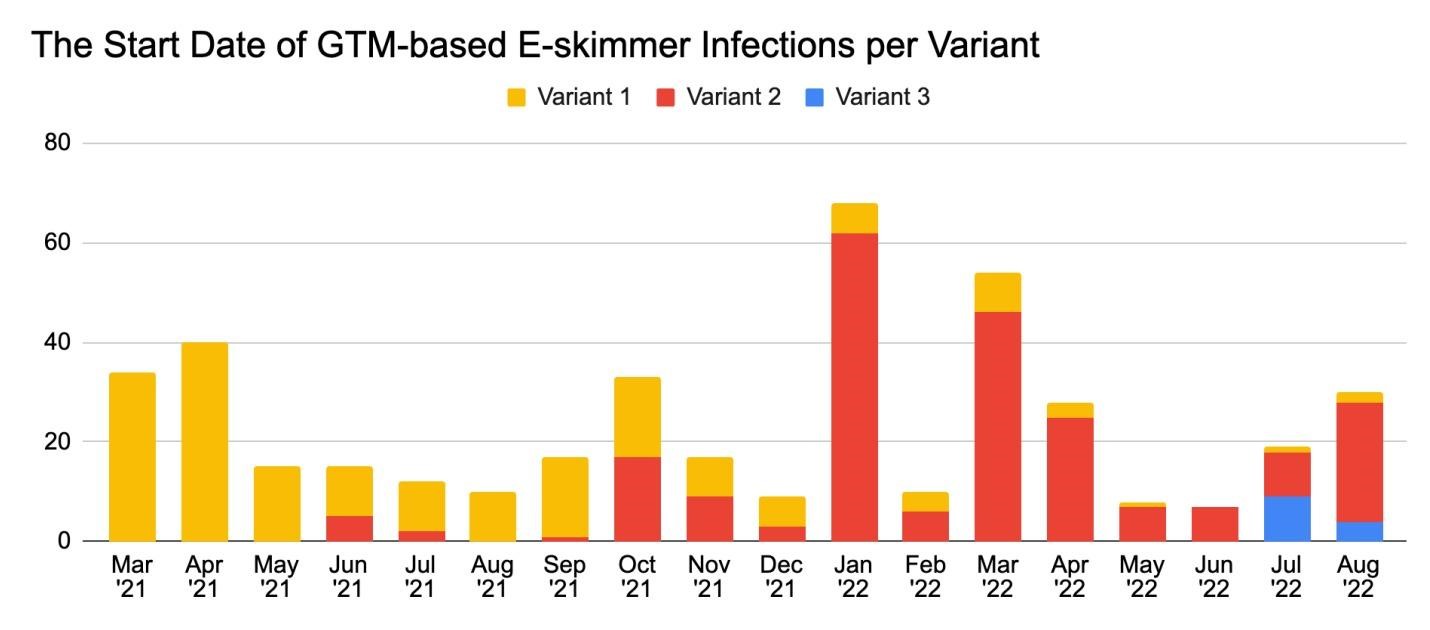
Recorded Future began tracking the use of three variants of GTM skimmers back in March 2021 and notes that new infected domains have been added every month since then.
The first and third versions of the skimmers have a certain similarity, which suggests that the same hackers are behind their creation and that they regularly update their tools to avoid detection.
At the same time, it is known that hackers are not only targeting “expensive” domains, which have more than a million visitors a month. Some of the sites that were attacked had only about 10,000 visitors.
Most of the affected sites are based in the US, accounting for more than 66% of infections. The rest have been found in Canada, Great Britain, Argentina, India, Italy, Australia, Brazil, Greece, Indonesia and other countries.

Leave a Comment