Akamai reports that in March 2022, a new P2P botnet Panchan appeared, which targets Linux servers (mainly in the educational sector) and mines cryptocurrency.
Let me remind you that we wrote that Operators of the Clipminer Botnet “Earned” More Than $1.7 Million, and also that 61% of malicious ads target Windows users.
Panchan is written in Go and has the functionality of an SSH worm, that is, it can perform dictionary attacks and abuse SSH keys to quickly move sideways on a compromised network.
In fact, Panchan infects new hosts by finding and using existing SSH keys, as well as by brute force logins and passwords. After success at this stage, it creates a hidden folder in which it hides under the name xinetd.
The malware then executes the binary and initiates an HTTPS POST to the Discord webhook, which is likely used to track the victim.
To gain a foothold in the system, Panchan copies itself to /bin/systemd-worker and creates a new systemd service to start after a reboot, that is, it disguises itself as a normal system service.
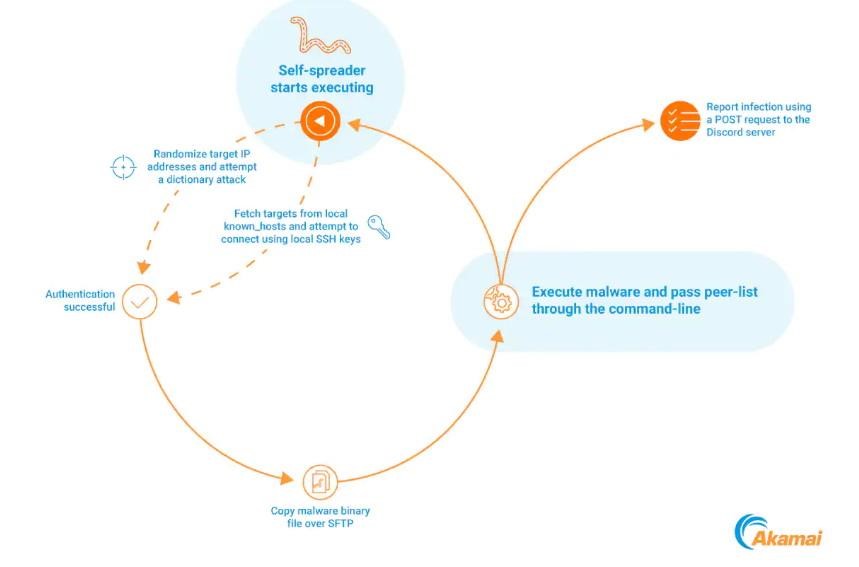
On the infected system, Panchan deploys and runs two miners, XMRig and nbhash, and the miners are not extracted to disk so as not to leave traces.
It is reported that in total, researchers were able to detect 209 peers in the Panchan P2P network, although only 40 of them are currently active, and these systems are mainly located in Asian countries.
The researchers say that most of the victims are related to the education sector, which matches the methods of distribution of malware and facilitates the growth of botent. The fact is that when conducting international academic research, ideal conditions are created for the spread of malware, because such projects are characterized by poor “digital hygiene” in the field of passwords and the sharing of SSH keys.

Leave a Comment